Entity - Relationship model
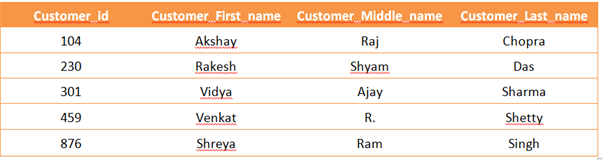
The E – R data model employs three notations: Entity sets, Relationship sets, and Attributes. 1. Entity sets An entity is a thing or object in real world that is different from other objects. For example, each employee in a company is an entity. An entity has a set of properties, and unique value for some properties. For example, the employee may have employee_id property whose value uniquely identifies the employee. Thus, 0201 value for employee_id would uniquely identify the employee in a company. An entity set is a set of entities of the same type that may share same properties, or attributes. For example, the set of all persons who are employees at a company can be defined as the entity set employee. Entity sets do not need to be disjoint. For example, a person may be an employee entity, a customer entity, both or neither. An entity is represented by set of attributes . Attributes are properties possessed by each member of the entity s...
