Entity - Relationship model
- Entity sets,
- Relationship sets, and
- Attributes.
1. Entity sets
An entity is a thing or object in real world that is
different from other objects. For example, each employee in a company is an
entity.
An entity has a set of properties, and unique value
for some properties. For example, the employee may have employee_id
property whose value uniquely identifies the employee. Thus, 0201 value for employee_id
would uniquely identify the employee in a company.
An entity set is a set of entities of
the same type that may share same properties, or attributes. For example, the
set of all persons who are employees at a company can be defined as the entity
set employee.
Entity sets do not need to be disjoint. For example, a
person may be an employee entity, a customer entity, both or neither.
An entity is represented by set of attributes.
Attributes are properties possessed by each member of the entity set. Each
entity may have its own unique value for each attribute. For example,
attributes of employee entity are employee_id, employee_name,
employee_address, employee_city, employee_pincode, employee_salary,
employee_designation, employee_phone_no.
Each entity has a value for each
attributes. The employee_id is used to uniquely identify the employees.
For each attribute, there is set of values, called the domain, or value set. A
database therefore includes a set of entity, each of which contain any number
of entities with same type.
An attribute, in the E – R model, can be categorized
by following attribute types:
Simple and composite attributes:
In our examples till now, the attributes have been
simple, hence cannot be further divided into subpart.
Composite attributes can be further divided into
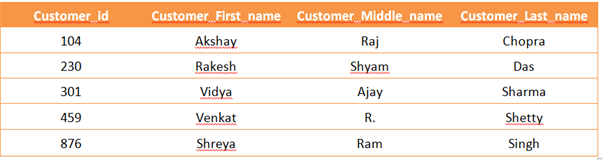
subparts. For example, the attribute name can be further divided as first_name,
middle_name and last_name.
Single – valued and multivalued attributes:
Derived attribute:
The attribute values are derived from the values of
other attributes or entities. For example, the employee entity set has an
attribute age to indicate the employee’s age. If date_of_birth
attribute is present in employee entity, then age calculation can be done.
Hence, age is a derived attribute. The value of derived attribute is not
stored, but evaluated whenever required.
An attribute takes null value when no
value is there for an entity. For example, if the employee does not have middle_name,
the null value can be assigned.
1.
Relationship sets
Association among entities is called relationship.
For example, we can define a relationship that associated employee shreya with
account number A – 5009.
A relationship set is a set of
relationships of same type. It is mathematical relation on n ≥ 2
(non-distinct) entity set. If E1, E2, ….., En
are entity sets, then a relationship set R is a subset of
{(e1, e2, …., en) | e1
∈ E1, e2 ∈ E2, …., en ∈ En}
Where, (e1, e2, …., en) is a relationship.
Figure – 1(a): Customer table
Figure – 1(b): Loan table
Figure – 2: An illustration of relationship set
borrower





Comments
Post a Comment